machine learning or automatic learning is the science that consists of making computers act without being explicitly programmed. Over the last ten years, automatic learning has allowed us to rise of several fields such as autonomous cars, speech recognition, effective search on the Web and understanding, considerably improved, of the human genome.
Can we conceive a machine having intellectual capacities equal to that of the human brain? Since Blaise Pascal and Von Leibniz, many scientists and engineers have asked themselves this same question.

Source: Pompe au net
Famous writers like Jules Verne, Frank Baum (OZ magician), Mary Shelley (Frankenstein), George Lucas (Star Wars) have imagined artificial beings with human behaviors.
Automatic learning is one of the most important branches of Artificial Intelligence (AI). Technology sector giants, such as Baidu and Google, have spent between 20 and 30 billion dollars in the field of AI in 2016: 90% in research and development, and 10% for AI acquisitions.
Today it is a real race to innovation and intellectual property
Let us however recall that this is not a recent field. Turing, Hebb, Samuel and Rosenblatt, among many others, paved the way for recent advances.
Machine Learning: What is it?
Probabilities, statistics and linear algebra at the service of data. It is a convergence of means implemented to model a set of data and discover an internal structure allowing to carry out the two main tasks: regression and classification. Any Machine Learning process can be broken down into three phases:
- Data preprocessing,
- Modeling,
- Deployment, maintenance.
Once the data cleaned and structured, they can be presented to machine learning algorithms;
Identify the type of problem
Categorize by input
- If the data are labeled, it is a supervised learning problem.
- If they are not and we are in search of a structure, it is a unsupervised learning problem.
Categorize by output
- If the output is a number, it is a regression problem.
- If the output is a class, it is a classification problem.
- If the output is an set of input groups, it is a clustering problem.
Machine learning
Two different learning types
Supervised learning
Learning phase: The data are presented having been previously labeled. Each entry is associated with an output value which can be numerical or categorical.
The algorithm then tries to find the rule allowing to relate the input (x) to the output (y), this is the predictive model that is built.
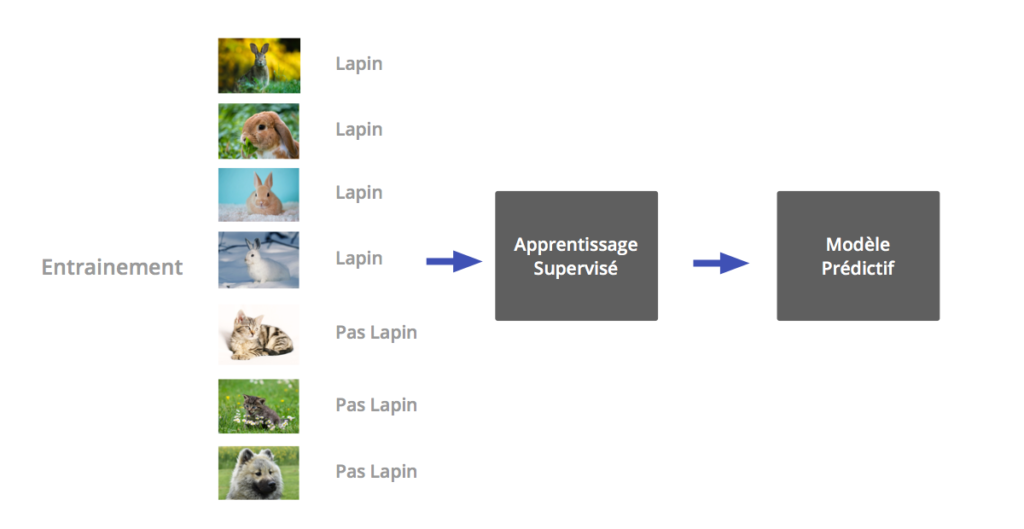
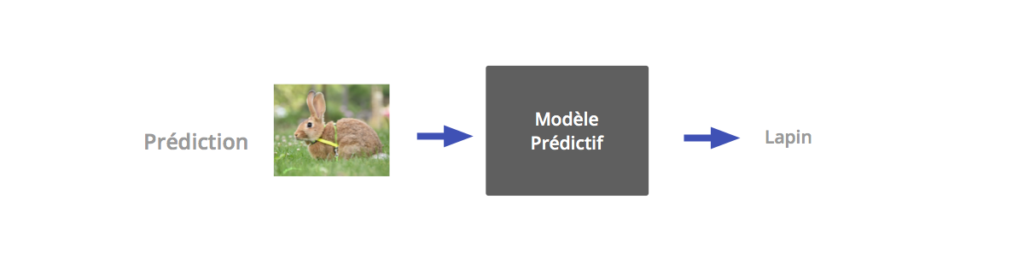
Prediction phase: We present a new entry to the model, the latter is charged with associating the correct output to it.
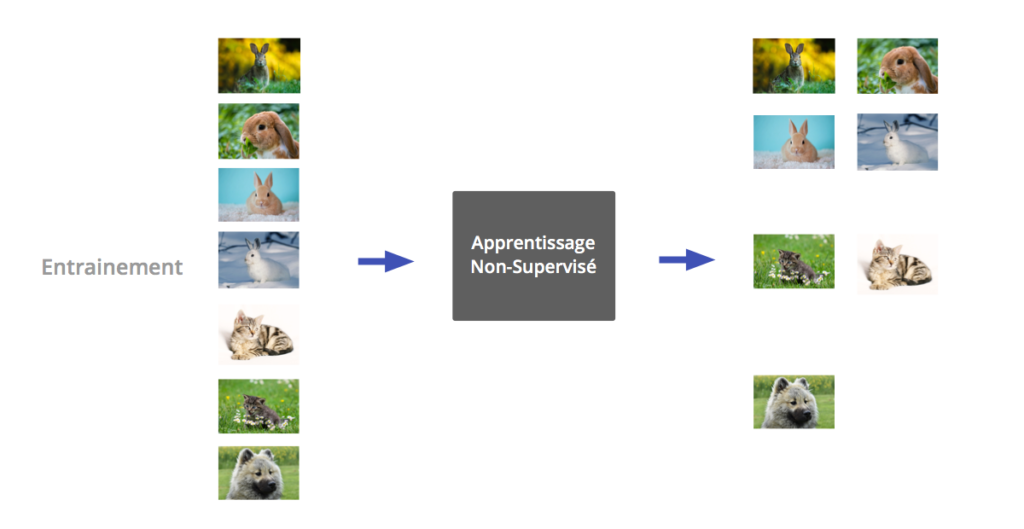
Unsupervised learning
In many situations, the data are not labeled. Unsupervised learning then allows discovering a hidden structure there. This is the clustering. The data are then grouped into a certain number of clusters.
Learning algorithm
Commonly used automatic learning algorithms
| Linear regression | The algorithm tries to find a linear relation between the input and the numerical output. |
| Logistic regression | This is a binary classifier built on a linear model associated with a sigmoid. |
| Decision trees | Structure of type organization chart in which each node is a test on an attribute and each branch represents the result of the test. |
| Random forest | This is a set of decision trees in which each tree trains on a part of data extracted in a random way. |
| Support vector machines | The data are represented in a space that allows to separate them by category. The new data are then placed in this same space and are then categorized. |
| KNN (K nearest neighbors) | This is the algorithm of k nearest neighbors. This is an unsupervised learning and the data are grouped according to the similarities that they may have with each other. |
How to choose them?
Now that the nature of the problem is well identified, it is time to select the appropriate algorithms. Numerous considerations are still to take into account such as:
Limitations of machine learning
The performance of algorithms of Machine Learning is no longer proven and they are today implemented in a multitude of processes. The arrival of Big Data has however posed some performance concerns to traditional learning mode. The data have become too voluminous and complex. The extraction of characteristics (" feature extraction") has then become a complex task, requiring the presence of a domain expert for a relevant selection of characteristics.
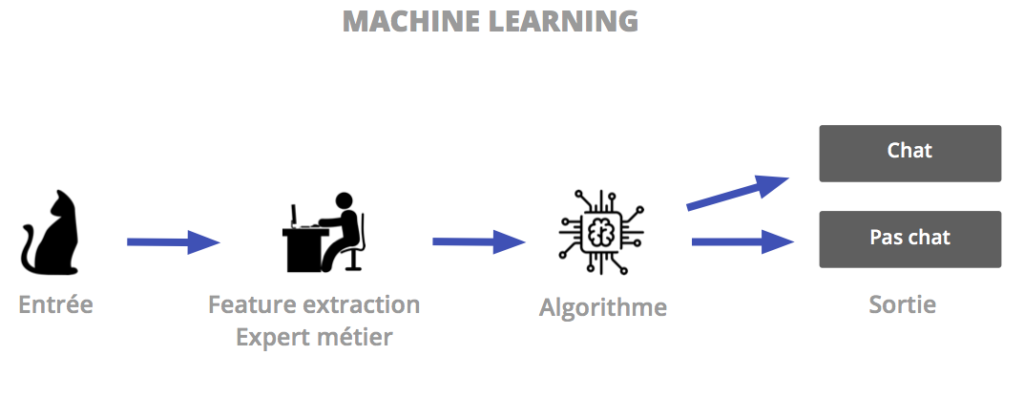
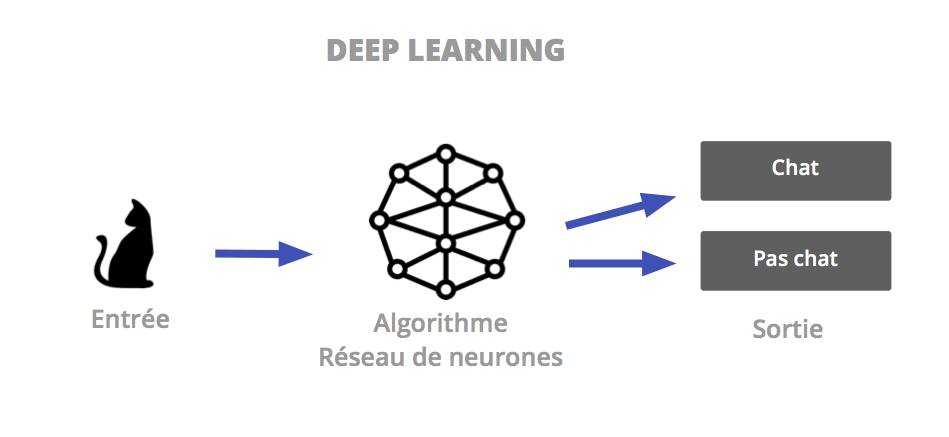
It is thus that the Deep Learning has imposed itself in recent years as a flagship method of Data Science. Deep learning brings us even closer to the functioning of the human brain and tackles the domains of vision, the natural language, but also sentiment analysis and empathy.